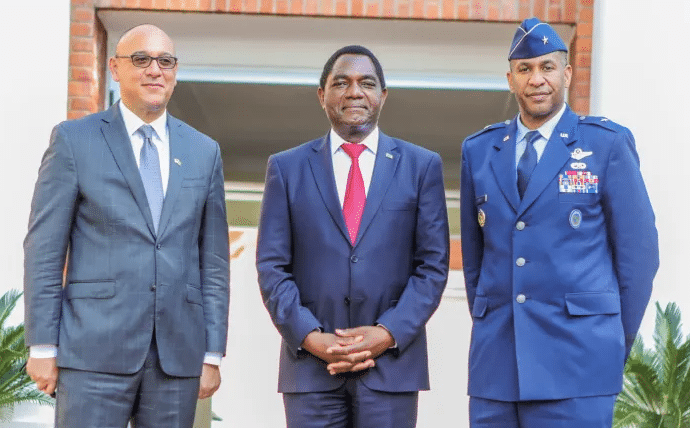
Brigadier General Peter Bailey, right, and U.S. Chargé d’Affaires to Zambia Martin Dale, left, with President Hakainde Hichilema, center. Source: zm.usembassy.gov.

Orinoco Tribune – News and opinion pieces about Venezuela and beyond
From Venezuela and made by Venezuelan Chavistas

Brigadier General Peter Bailey, right, and U.S. Chargé d’Affaires to Zambia Martin Dale, left, with President Hakainde Hichilema, center. Source: zm.usembassy.gov.
By Jeremy Kuzmarov – May 9, 2022
Because of Zambia’s Copper and to Thwart the Chinese
On April 25, the U.S. government announced that U.S. African Command (AFRICOM) will open an Office of Security Cooperation at the U.S. Embassy in Zambia.
Brigadier General Peter Bailey, AFRICOM’s Deputy Director for Strategy, Engagement, and Programs, made the announcement in Zambia during a meeting with Zambian President Hakainde Hichilema (HH), who took office on August 21, 2021.
According to AFRICOM, the new Office of Security Cooperation will “enhance military-to-military relations [between AFRICOM and Zambian armed forces] and expand areas of cooperation in force management, modernization and professional military education for the Zambian security forces.”
The U.S. government possesses a giant embassy in Lusaka and, since 2014, has invested more than $8 million in assistance for Zambian battalions deployed to a United Nations peacekeeping mission in the Central African Republic (CAR).


Emmanuel Mwamba, Zambia’s former representative to the African Union (AU), had tried to block AFRICOM’s expansion into Zambia, following the precedent of Zambia’s last four presidents (Levy Mwanawasa, Rupiah Banda, Michael Sata and Edgar Lungu).
Mwamba emphasized that, since obtaining its independence from Great Britain in 1964, Zambia has promoted a non-aligned policy and cooperated with all powers, including Russia and China as well as the U.S.



The U.S. interests and motivations underlying the AFRICOM expansion in Zambia are not hard to discern.
As CAM previously reported, Zambia is one of the world’s leading producers of copper, which according to a recent Goldman Sachs report, Copper is the New Oil, is crucial in the transition to a clean energy economy.
Copper is a key electrical conductor and component for solar and wind power plants, electric vehicles and batteries, and energy-efficient buildings.
Hichilema was favored by the U.S. State Department in Zambia’s August 2021 election because of his pledge to boost domestic refining capabilities and loosen regulations and lower taxes on foreign mining companies operating in Zambia to enable a $2 billion expansion of copper production.
One of the big beneficiaries of the new policies is Barrick Gold, a Canadian company which owns the $735 million Lumwana copper mine in Solwezi and is poised to expand its operations.

Its founder and CEO, Laurence Fink, was a donor to Barack Obama, Hillary Clinton, Chuck Schumer and John Kerry, along with Paul Ryan and other Republican and Democratic Party politicians who supported the expansion of AFRICOM.

BlackRock further invested in Glencore and Vedanta Resources, which own additional Zambian copper mines and, like the others, have checkered records when it comes to workers’ rights and the environment.

AFRICOM was established in 2007 with the official purpose of promoting a “stable and secure African environment in support of U.S. foreign policy.”
Today, AFRICOM sustains ties with 53 African nations and provides a cover for an estimated 9,000 U.S. troops stationed in Africa and at least 27 military bases.


Tied to the motive of natural resources exploitation underlying AFRICOM’s expansion into Zambia is the growing geopolitical competition with China.
Zambia has been a significant recipient of China’s Belt and Road Initiative and, in 2018, the volume of China-Zambia bilateral trade reached $5 billion in U.S. dollars, with a year-on-year growth of 33.9%.
As of December 2020, more than 600 Chinese companies operated in Zambia, the majority in the Copperbelt. Zambia even boasts two Chinese-built special economic zones and allowed banking in the Chinese renminbi instead of the kwacha, dollar, or euro to facilitate trade with China.

The danger of the AFRICOM expansion for Zambians is palpable not only in its function in protecting foreign control of its economy but aso in generating potential political instability.
According to Black Agenda Report, troops trained by AFRICOM have been behind nine coup d’états in Africa since AFRICOM’s formation.
Zambia could be next, particularly if Hichilema reverses his current policies in the mining sector, or if copper prices fluctuate because of some unforeseen event and Zambia’s economy falters more than it already has.
Featured image: Brigadier General Peter Bailey, right, and U.S. Chargé d’Affaires to Zambia Martin Dale, left, with President Hakainde Hichilema, center. Source: zm.usembassy.gov.

Jeremy Kuzmarov is Managing Editor of CovertAction Magazine. He is the author of four books on US foreign policy, including Obama’s Unending Wars (Clarity Press, 2019) and The Russians Are Coming, Again, with John Marciano (Monthly Review Press, 2018).
You must be logged in to post a comment.